This is an excerpt from a recent post on Subtopia about an Australian immigration detention center being built on Christmas Island. I was particularly attracted to the technology involved in detaining immigrants. This is not exactly pleasant reading…
Since 2005 Australiaâ??s Department of Immigration has been constructing an “Immigration Reception and Processing Centre.” 2,400 km from Perth, 360 km from Jakarta and nearly 2000 km from Darwin, this deteniton complex is at the far end of the island which, according to this dispatch, is a narrow strip 24 km long and 7 km wide.
Keep in mind, as Angela tells us, â??under Australian law it is possible to intern people extra-judicially (without trial or charge) and, since 2004, to do so indefinitely. Migration detention is, therefore, a wholly administrative matter.â??
So just what exactly are they building out there in them pristine jungles?
Well, it turns out itâ??s not just some rinky dink detention outfit with some barbed-wire fencing and ramshackle barracks cliff-side. No, this is a $396 million tropical prison paradise. Thatâ??s right. For what the government refers to as a â??deterrent to illegal immigrationâ??, it is a state of the art 800-bed prison complex, with electric fences, movement detectors, hundreds of surveillance cameras, hidden microphones in the trees, the works.

[Image: “Camp Howard” – Australia’s very own Guantanamo Bay on Christmas Island, Feb. 2007.]â??The camp on Christmas Island has CCTV linked to a RCR [Remote Control Room] so guards in Canberra can watch detainees around the clock.â?? And planners arenâ??t leaving any thing out for this rugged remote little island prison either. â??Detainees will wear electronic ID tags or cards, identifying them wherever they are.â?? While the place crawls with guards wandering in between a perimeter of checkpoint cubicles, there is a hospital, operating theatre and visiting rooms, solitary cells, and even family units and a nursery. â??Everything can be controlled remotely â?? doors, TV, radio.â??
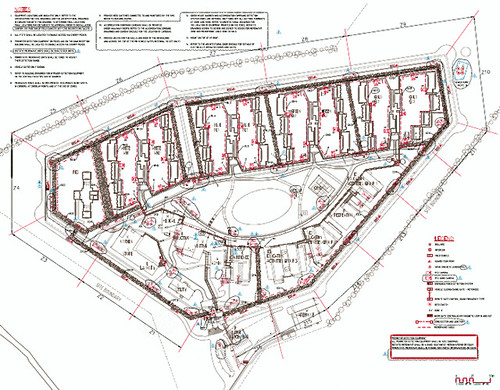
{Image: Floor plan for the Detention Facility at Christmas Island.]In addition to developing this offshore island-chain barrier against migration, the Australian government has launched its border patrol ship, the Triton, dubbed the â??prison shipâ?? by critics. This â??98-metre trimaranâ?? is said to be capable of detaining â??30 people for up to a month” on board and is “armed with twin machine guns.â??

[Image: The ACV Triton Australian Border Patrol Ship.]While officially deployed to patrol and intercept illegal fisherman, others are more concerned what the Triton could mean for migrants stranded at sea already facing one of the most conservative immigration-tolerant nations in the world.
Update: The last line should probably read immigration-intolerant…

