There I was calmly at home with the laptop, well prepared for the impending winter storm that is going to hit us soon when I got a message from a friend via Facebook telling me that there is a fake twitter account in my name. The message included a link to this account
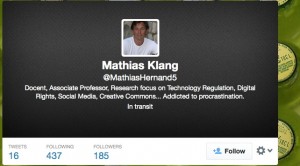
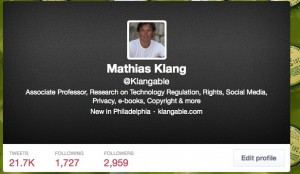
At first I didn’t spot it. All I saw was the number of tweets, following and followers were wrong. Then I saw that the text was wrong, before I finally saw the twitter handle was another. Here is my twitter account
Not only had the cheeky bugger stolen my image and my (older) bio but even taken my background too. Damn! He/she has also violated the Creative Commons license for my image of the bottles in the background. No attribution!
He/she has been tweeting since August and only managed 16 tweets. But the last one was just hours ago. Why? Seriously It can’t be that difficult to create a profile – so is to somehow fool my friends? I doubt that would work.
Anyway I filed a complaint with twitter and quickly received a mail with the content
To confirm your identity, fax a copy of your valid government-issued photo ID (e.g., driver’s license, passport) to Twitter
Really!! Not only do I have to prove that I am who I am, but now I have to find two pieces of archaic technology (photocopier and fax) in order to prove who I am.
What this proves is:
- Stealing someones likeness and bio is easy online (duh!)
- In order to really prove who we are we need to downgrade to pre-internet technology
- First world problems are really a drag